Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) affects approximately 1 in 36 children in the U.S., representing a rapidly growing and underserved population.
Despite advances in diagnosis, there remain no FDA-approved pharmacologic treatments targeting the core social and communication challenges of autism.
This need presents an opportunity for innovation and clinical impact through novel, evidence-based therapeutic approaches.
Autism Spectrum Disorder
Innovative Treatment Discovery —
Ethosuximide
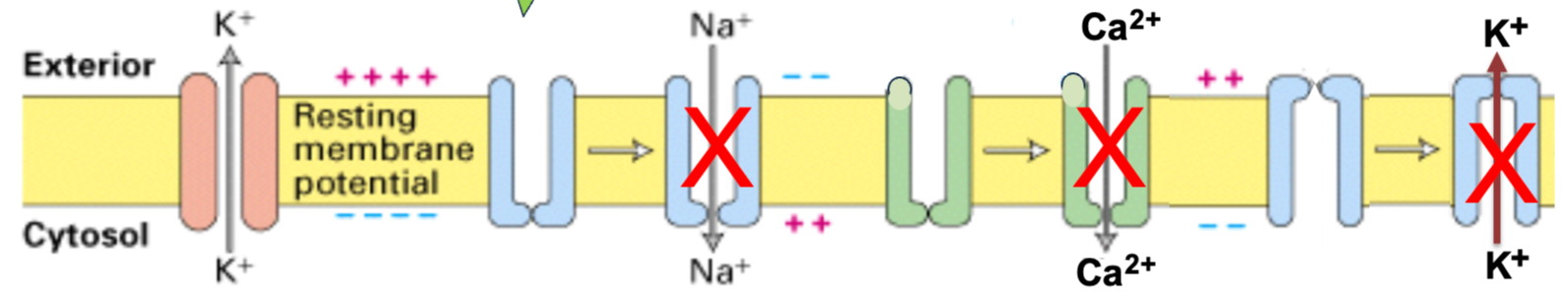
Ethosuximide’s Mechanism of Action
Ethosuximide regulates neuronal excitability by reducing activity of voltage-dependent ion channels (T-type Ca 2+ channels, sustained Na+ channels, and Ca 2+-dependent K+ channels)
In an animal model T-type channel reduces autism spectrum disorder behavior
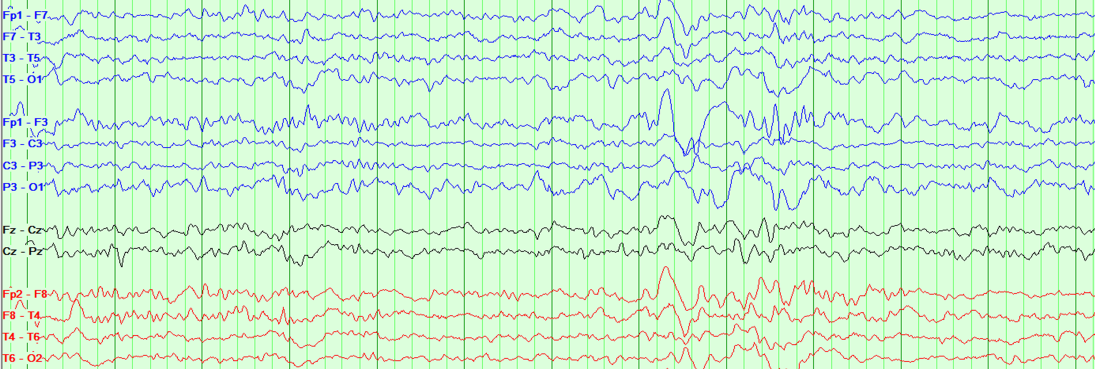
Ethosuximide’s Effect on EEG of Subjects with ASD
Sample EEG Recording
Theory of Autism Spectrum Disorder
A leading theory of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) proposes that the condition arises from imbalanced connectivity between brain regions, disrupting how neural networks communicate and process information.
Ethosuximide may help restore this balance by selectively modulating specific neural connections.
Ethosuximide’s Effect
Using quantitative EEG analysis (spectral power, coherence, and entropy) we can detect these connectivity changes, providing objective biomarkers of therapeutic response.